Qiskit SDK version strategy
Qiskit version numbers follow Semantic Versioning.
The version number is comprised of three primary components: the major, minor, and
patch versions. For example, in version number X.Y.Z, X is the major version,
Y is the minor version, and Z is the patch version.
Breaking API changes are reserved for major version releases. The minimum period between major version releases is one year. Minor versions introduce new features and bug fixes without breaking API compatibility, and are periodically (currently every three months) published for only the current major version. Patch versions provide fixes for bugs identified in the most recent minor version of each actively supported release series (that is, the major version). We support at most two release series at a time, which occurs only during the period of overlap following a new major version release, described in more detail below.
Release schedule
A tentative release schedule is included below:
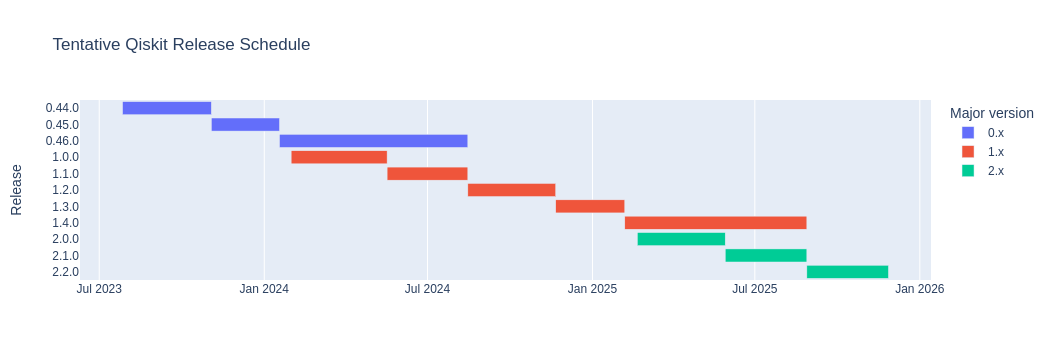
For an up-to-date release schedule, refer to the Qiskit Github project's milestones list, which will always contain the current release plan.
With the release of a new major version, the previous major version is supported for at least six months; only bug and security fixes are accepted during this time and only patch releases are published for this major version. A final patch version is published when support is dropped, and that release also documents the end of support for that major version series. A longer support window is needed for the previous major version as this gives downstream Qiskit consumers and their users a chance to migrate their code. Downstream libraries that depend on Qiskit should not raise their minimum required Qiskit version to a new major version immediately after its release because the library's user base needs time to migrate to the new API changes. Having an extended support window for the previous major Qiskit version gives downstream projects time to ensure compatibility with the next major version. Downstream projects can provide support for two release series at a time to give their users a migration path.
For the purposes of semantic versioning, the Qiskit public API is considered
any documented module, class, function, or method that is not marked as private
(with an underscore _ prefix). However, there can be explicit exceptions made for
specific documented APIs. In such cases, these APIs will be clearly documented
as not being considered stable interfaces yet, and a user-visible warning will be
actively emitted on any use of these unstable interfaces. Additionally, in some
situations, an interface marked as private is considered part of the public
API. Typically this only occurs in two cases: either an abstract interface
definition where subclasses are intended to override/implement a private method
as part of defining an implementation of the interface, or advanced-usage
low-level methods that have stable interfaces but are not considered safe to use,
as the burden is on the user to uphold the class/safety invariants themselves
(the canonical example of this is the QuantumCircuit._append method).
The supported Python versions, minimum supported Rust version (for building Qiskit from source), and any Python package dependencies (including the minimum supported versions of dependencies) used by Qiskit are not part of the backwards compatibility guarantees and may change during any release. Only minor or major version releases will raise minimum requirements for using or building Qiskit (including adding new dependencies), but patch fixes might include support for new versions of Python or other dependencies. Usually the minimum version of a dependency is only increased when older dependency versions go out of support or when it is not possible to maintain compatibility with the latest release of the dependency and the older version.
Upgrade strategy
When a new major version is released, the recommended upgrade path
is to first upgrade to the most recent minor version on the previous major
version. Shortly before a new major version, a final minor version will
be published. This final minor version release X.Y+1.0.0 is equivalent to
X.Y.0 but with warnings and deprecations for any API changes that are
made on the new major version series.
For example, immediately proceeding the 1.0.0 release, a 0.46.0 release will be published. The 0.46.0 release will be equivalent to the 0.45.0 release but with additional deprecation warnings that document the API changes that were made as part of the 1.0.0 release. This pattern will be used for any future major version releases.
Qiskit users should first upgrade to this final minor
version to see any deprecation warnings and adjust their Qiskit
usage before trying a potentially breaking release. The previous
major version will be supported for at least six months to give sufficient time
to upgrade. A typical pattern to manage this is to pin the maximum version to
avoid using the next major release series until you're sure of compatibility.
For example, specifying qiskit<2 in a requirements file when the current
major Qiskit version is 1 ensures that you're using a version of Qiskit
that doesn't have breaking API changes.
Capping the version less than the next major version
ensures that you see any deprecation warnings before a
major version release.
Without the cap, pip installs
the newest version available by default.
The QPY serialization format is backwards-compatible so that a new Qiskit release can always load a QPY
file generated with an earlier release of Qiskit. However, the format isn't forward-compatible so, in principle, it's not possible
to load QPY files generated with a newer version of Qiskit using an older release. To facilitate user migration across major version releases, the qiskit.qpy.dump() function will always support at least one overlapping version between the X.0.0 and the X-1.Y.0 release (where Y is the last minor version of
that series). The parameter qiskit.qpy.dump(..., version=...) will enable saving QPY format files that can be loaded by both major versions from the newer
release. See more details in RFC 0020.
Pre-releases
For each minor and major version release, Qiskit publishes pre-releases that
are compatible with PEP440. Typically
these are release candidates of the form X.Y.0rc1. The rc releases
will have a finalized API surface and are used to test a prospective release.
Note that when one of the PEP440 pre-release suffixes (such as a, b, or pre) are
published, it does not have the same guarantees as an rc release, and is
only a preview release. The API might change between these pre-releases
and the final release with that version number. For example, 1.0.0pre1 might have
a different final API than 1.0.0.
Post-releases
If there are issues with a release's packaging, a post-release might be
issued to correct this. These will follow the form X.Y.Z.1 where the fourth
integer indicates that it is the first post-release of the X.Y.Z release.
For example, the qiskit-terra (the legacy package name for Qiskit) 0.25.2
release had some issue with the sdist package publishing, and a post-release
0.25.2.1 was published that corrected this issue. The code was identical, and
0.25.2.1 only fixed the packaging issue for the release.
How contributors can mark deprecations
Refer to the deprecation guide in the Qiskit SDK repository for instructions on how to add deprecations to the source code.